
Serverless image classification with Azure Functions and Custom Vision – Part 4
In this article, you will deploy a function project to Azure using Visual Studio Code to create a serverless HTTP API.

Welcome to the third part of the learning series “Serverless image classification with Azure Functions and Custom Vision”! In the previous articles, you built an image classification model that predicts whether a photo contains a dog or a cat and exported the Custom AI model to a TensorFlow file to run offline.
To find out more about previous posts, check out the links below:
In this article, you are going to create an “intelligent” Python function that responds to HTTP requests and classifies images. You will learn how to:
To complete the exercise, you will need:
Choose the Azure icon in the left toolbar bar and next to Workspace (local), select the + button. In the dropdown window, choose Create Function.
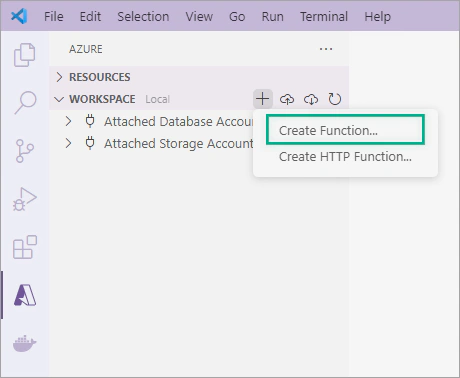
Choose the directory for your project.
In the Select a language window, choose Python and then choose your preferred Python interpreter.
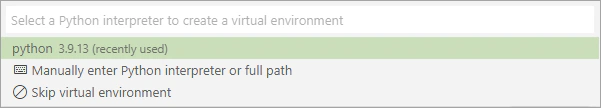
Choose the HTTP trigger template for your project’s first function.
Provide a name for your function, for example, enter classify.
Then, in the Authorization level window, choose Anonymous, which lets anyone call your function.

Wait for your Azure Functions project to be generated. Visual Studio Code will create a function in your chosen language using the HTTP trigger template.
Your function project contains several files. In the following sections of this tutorial, we will edit these files:
requirements.txt: A project-level file that lists the Python packages required by Azure Functions.__init__.py: A Python file that contains the function’s code and is in the classify folder.Before editing the function’s code, let’s run the function locally!
In the left toolbar, select the Run and Debug icon. To start the function locally, select the play icon (Start Debugging) or press F5.
In the Terminal, you can see the endpoint of your local function.
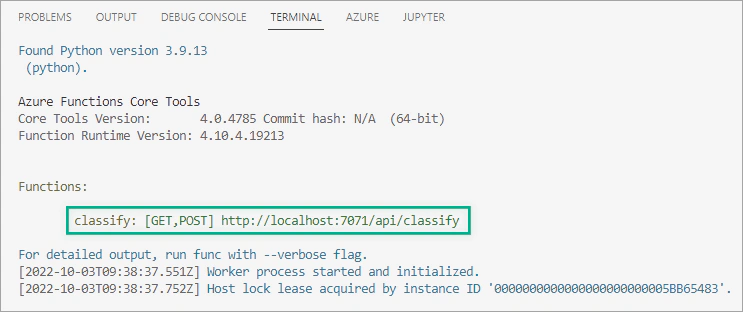
Choose the Azure icon, right-click on the classify function and select Execute Function Now.
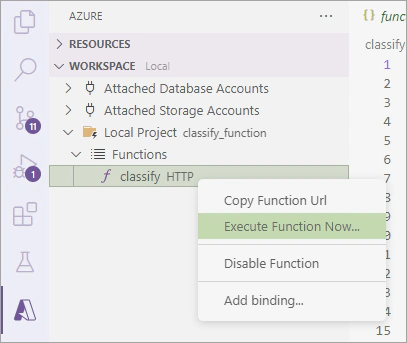
In the Enter request body window, leave the default values and press Enter.

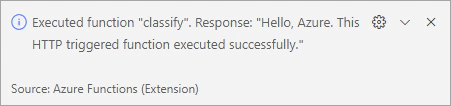
If the function runs correctly, a notification is raised in Visual Studio Code containing information about the function’s execution.
To modify the classify function to predict whether an image contains a cat or a dog, you will use the custom TensorFlow model exported from Azure Custom Vision and the predict.py script that you created in the previous article.
In the classify folder, copy the model files into a new folder named model. Verify that the model folder contains these files: model.pb and labels.txt.
Copy the predict.py file (which contains code to run the TensorFlow model) into the classify folder.
Open the requirements.txt file and add the following Python libraries:
| |
Open the __init__.py file and after the existing import statements, import the helper function for the predict.py script.
| |
Replace the contents of the main function with the following code, which retrieves the submitted image URL, calls the predict_image_from_url() function to classify the image using the TensorFlow model, and returns an HTTP response with the predicted label and its probability.
| |
Then, run the function to install the required dependencies and review the function’s response.

http://localhost:7071/api/classify?img=<URL>.In this article, you learned how to use Python, TensorFlow, and Visual Studio Code to build a function that predicts whether an image contains a cat or a dog. In the next part of this series, you will learn how to publish your Azure Functions project to Azure to build a serverless HTTP API.
If you are interested in learning more about Azure Functions, you may check out the following resources:

In this article, you will deploy a function project to Azure using Visual Studio Code to create a serverless HTTP API.
In this article, you will learn how to export a Custom Vision model programmatically using the Python client library.
In this article, you will learn how to export a Custom Vision model in TensorFlow format for use with Python apps.
This article will show you how to export your classifier using the Custom Vision SDK for Python and use the model to classify images.